
Specialized company in manufacturing steel ball & tapered roller for precise ball bearings
HomeReferenceTechnical Data

This is mainly standardized for the steel balls of the ball bearings which is used for rolling elements of ball bearings.
The term, symbols, and meaning of terms used in this standard are as follows.
It is a standard dimension which is widely used to show the size of the steel ball.
A diameter value used for showing that the size of the steel ball is normally the same.
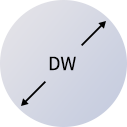
Distance between the two parallel planes contacting the actual surface of one steel ball
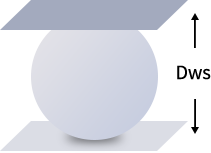
The average of the maximum and minimum diameter of a single steel ball

Difference between maximum and minimum diameter value of a single steel ball

The maximum distance at the radius distance of each point on the steel ball
A certain quantity of steel balls manufactured under the same conditions and treated as the same product
The average of the diameter in a single lot

The difference between the maximum steel ball average diameter and the minimum steel ball average diameter

A certain combination of size, precision of shape, surface roughness, and interval precision. It is indicated by the grade number.
As a difference between the average diameter and the nominal diameter of a lot, it is one of the group values determined by grade
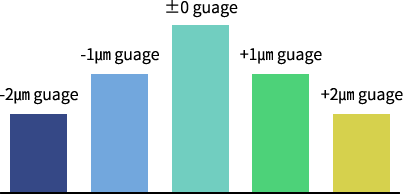
Difference among the close gauges determined by grade
Difference of lot average diameter and nominal diameter
As a surface irregularities generated in a small space, it is generated by manufacturing method or other influential factors.
※ These irregularities are generally considered within the determined interval. For example, it is calculated within distance of standard dimension.Surface irregularities which are periodic or irregular, deviating from an ideal sphere shape
※ This waviness depends on the size of the speed, and the waviness is divided according to the filter.As a measurement of resistance hardness against surface pressing, it is implemented through a determined method.